
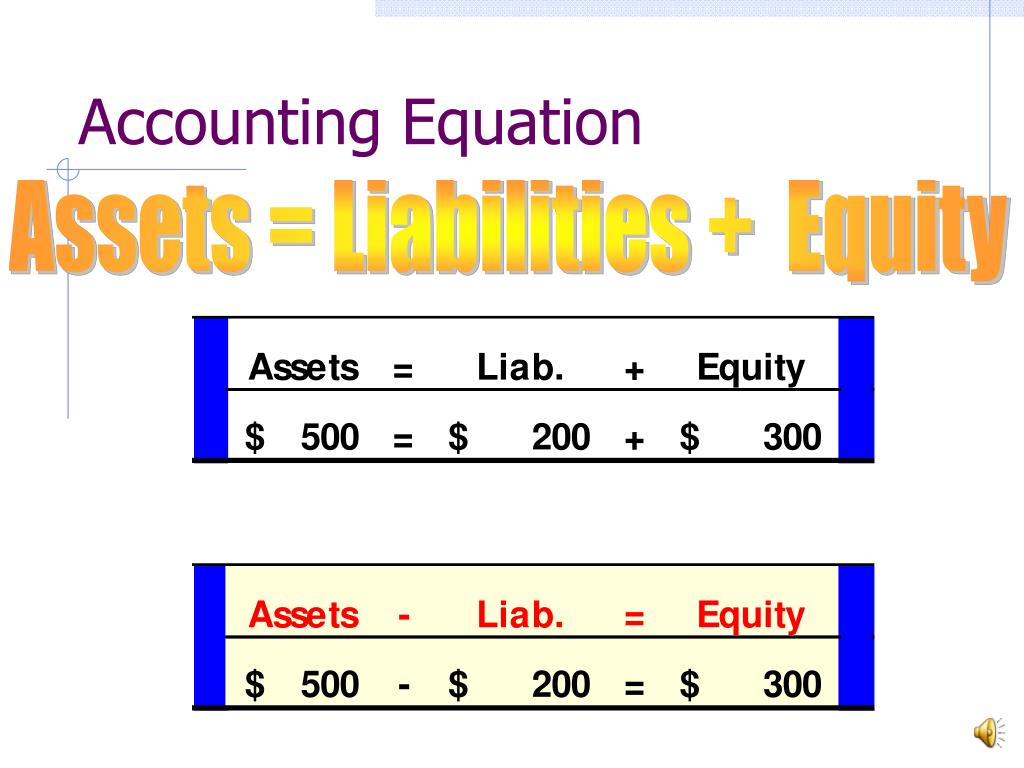
The purpose of this article is to consider the fundamentals of the accounting equation and to demonstrate how it works when applied to various transactions. All assets owned by a business are acquired with the funds supplied either by creditors or by owner(s). In other words, we can say that the value of assets in a business is always equal to the sum of the value of liabilities and owner’s equity. The total dollar amounts of two sides of accounting equation are always equal because they represent two different views of the same thing.
Impact of transactions on accounting equation
If a company keeps accurate records using the double-entry system, the accounting equation will always be “in balance,” meaning the left side of the equation will be equal to the right side. The balance is maintained because every business transaction affects at least two of a company’s accounts. For example, when a company borrows money from a bank, the company’s assets will increase and its liabilities will increase by the same amount. When a company purchases inventory for cash, one asset will increase and one asset will decrease. Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction, the accounting system is referred to as the double-entry accounting or bookkeeping system.
Let’s add transaction #3:
Liabilities refer to debts or obligations owed by the business. They are a particular amount owed to creditors of the business. Examples of liabilities include accounts payable, bank loans, and taxes. Before explaining what this means and why the accounting equation should always balance, let’s review the meaning of the terms assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity. As you can see, assets equal the sum of liabilities and owner’s equity.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
- This simple formula can also be expressed in three other ways, which we’ll cover next.
- Understanding how to use the formula is a crucial skill for accountants because it’s a quick way to check the accuracy of transaction records .
- Thus, the accounting equation is an essential step in determining company profitability.
- We will now consider an example with various transactions within a business to see how each has a dual aspect and to demonstrate the cumulative effect on the accounting equation.
For every business, the sum of the rights to the properties is equal to the sum of properties owned. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. To learn more about the balance sheet, see our Balance Sheet Outline. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
Anushka will record revenue (income) of $400 for the sale made. A trade receivable (asset) will be recorded to represent Anushka’s right to receive $400 of cash from the customer in the future. As inventory (asset) has now been sold, it must be removed from the accounting records and a cost of sales (expense) figure recorded. The cost of this sale will be the cost of the 10 units of inventory sold which is $250 (10 units x $25). The difference between the $400 income and $250 cost of sales represents a profit of $150.
What Is a Liability in the Accounting Equation?
On the other hand, equity refers to shareholder’s or owner’s equity, which is how much the shareholder or owner has staked into the company. Small business owners typically have a 100% stake in their company, while growing businesses may have an investor and share 20%. Plus, errors are more likely to occur and be missed with single-entry 6 benefits of mobile apps for small businesses accounting, whereas double-entry accounting provides checks and balances that catch clerical errors and fraud. Liabilities are the amounts of money the company owes to others. Think of liabilities as obligations — the company has an obligation to make payments on loans or mortgages or they risk damage to their credit and business.
This is what ensures that every transaction makes sense and there will always be an entry on both sides of each transaction. The third part of the accounting equation is shareholder equity. The revenue a company shareholder can claim after debts have been paid is Shareholder Equity. The accounting equation states that the amount of assets must be equal to liabilities plus shareholder or owner equity. On 5 January, Sam purchases merchandise for $20,000 on credit.
Shareholders’ equity is the total value of the company expressed in dollars. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them.
An asset is a resource that is owned or controlled by the company to be used for future benefits. Some assets are tangible like cash while others are theoretical or intangible like goodwill or copyrights. This arrangement can be ideal for sole proprietorships (usually unincorporated businesses owned by one person) in which there is no legal distinction between the owner and the business. For example, John Smith may own a landscaping company called John Smith’s Landscaping, where he performs most — if not all — the jobs.
11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. The effects of changes in the items of the equation can be shown by the use of + or – signs placed against the affected items. Both these arrangements mean the same thing – one just has fewer steps and may be easier to digest for those who aren’t yet familiar with the formula. Still, let’s dive into the differences between the two so that you can understand how each might affect your bookkeeping process.
On 28 January, merchandise costing $5,500 are destroyed by fire. The effect of this transaction on the accounting equation is the same as that of loss by fire that occurred on January 20. On 10 January, Sam Enterprises sells merchandise for $10,000 cash and earns a profit of $1,000. As a result of this transaction, an asset (i.e., cash) increases by $10,000 while another asset ( i.e., merchandise) decreases by $9,000 (the original cost). The combined balance of liabilities and capital is also at $50,000.




