
A company’s quarterly and annual reports are basically derived directly from the accounting equations used in bookkeeping practices. These equations, entered in a business’s general ledger, will provide the material that eventually makes up the foundation of a business’s financial statements. This includes expense reports, cash flow and salary and company investments. Under the accrual basis of accounting, expenses are matched with revenues on the income statement when the expenses expire or title has transferred to the buyer, rather than at the time when expenses are paid.
- If it’s financed through debt, it’ll show as a liability, but if it’s financed through issuing equity shares to investors, it’ll show in shareholders’ equity.
- The balance sheet is also known as the statement of financial position and it reflects the accounting equation.
- Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners.
Effect of Transactions on the Accounting Equation
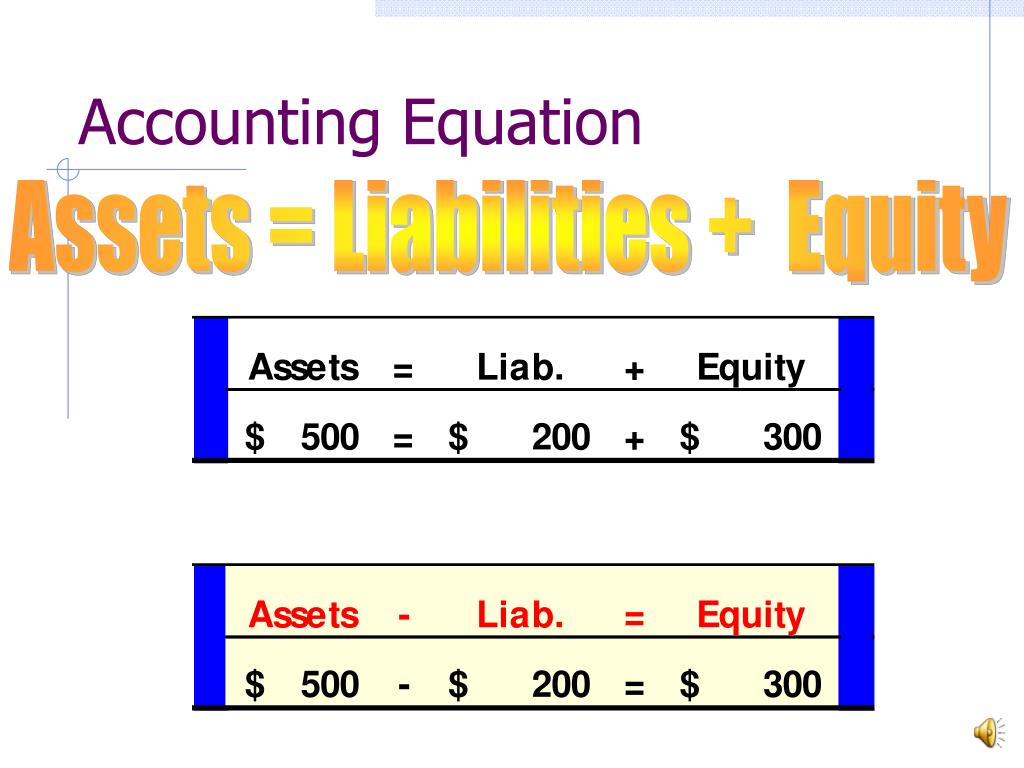
After saving up money for a year, Ted decides it is time to officially start his business. He forms Speakers, Inc. and contributes $100,000 to the company in exchange for all of its newly issued shares. This business transaction increases company cash and increases equity by the same amount. The accounting equation is also called the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. Notice that every transaction results in an equal effect to assets and liabilities plus capital.
What are assets?
It offers a quick, no-frills answer to keeping your assets versus liabilities in balance. Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital (assets) to all sources of capital, where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity. The assets of the business will increase by $12,000 as a result of acquiring the van (asset) but will also decrease by an equal amount due to the payment of cash (asset). Capital essentially represents how much the owners have invested into the business along with any accumulated retained profits or losses. The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner. The Accounting Equation is a vital formula to understand and consider when it comes to the financial health of your business.
Balance Sheet and Income Statement
As a core concept in modern accounting, this provides the basis for keeping a company’s books balanced across a given accounting cycle. The income statement is the financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses and the resulting net income. While the balance sheet is concerned with one point in time, the income statement covers a time interval or period of time. The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. As you can see, no matter what the transaction is, the accounting equation will always balance because each transaction has a dual aspect.
This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1. In this example, we will see how this accounting equation will transform once we consider the effects of transactions from the first month of Laura’s business. The accounting equation shows the amount of resources available to a business on the left side (Assets) and those who have a claim on those resources on the right side (Liabilities + Equity).
Obligations owed to other companies and people are considered liabilities and can be categorized as current and long-term liabilities. An asset can be cash or something that has monetary value such as inventory, furniture, equipment etc. while liabilities are debts that need to be paid in the future. For example, if you have a house then that is an asset for you but it is also a liability because it needs to be paid off in the future. On the other side of the equation, a liability (i.e., accounts payable) is created. Creditors have preferential rights over the assets of the business, and so it is appropriate to place liabilities before the capital or owner’s equity in the equation.
This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is considered to be the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced. That is, each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry (or coverage) on the credit side.
One of the main financial statements (along with the balance sheet, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity). The income statement is also referred to as the profit and loss statement, P&L, statement of income, and the statement of operations. The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading of the statement. If a company’s stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement. Because it considers assets, liabilities, and equity (also known as shareholders’ equity or owner’s equity), this xero time tracking and invoicing integration is the basis of a business’s balance sheet. The accounting equation is based on the premise that the sum of a company’s assets is equal to its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity.




